Credit system for undergraduate students in SCE
SCE is dedicated to nurturing students with solid foundation, wide knowledge and strong capability in Civil Engineering, Construction Management, Engineering Mechanics, Water Engineering and Smart Construction. The students are qualified to be registered engineers with high innovation abilities in areas of design, construction, management or research. In the education system, each student needs to acquire 165 credits to obtain a Bachelor's degree. The courses are classified as required courses, selected courses and cultural courses. The credit system for SCE undergraduate students is presented in Table 2-1.
Major | Required Courses | Selected Courses | Cultural Courses | Total |
Civil Engineering | 139.5 | 19.5 | 6 | 165 |
Construction Management | 127 | 32 | 6 | 165 |
Engineering Mechanics | 131.5 | 27.5 | 6 | 165 |
Water Engineering | 131 | 28 | 6 | 165 |
Smart Construction | 135.5 | 23.5 | 6 | 165 |
Note: the numbers in the table refer to the credits required in each major
According to SEU credit system, a comprehensive course system is designed for the undergraduate students in Civil Engineering, Construction Management, Engineering Mechanics, Water Engineering and Smart Construction, as shown in Fig. 2-1 (The English and Chinese names of all the courses are shown in Appendix II). The courses are arranged from fundamentals to applications during the four years of study. Each year, there are three semesters, in which the first semester is designed for short-term workshops or internships with a 1-month duration, and the other two are the spring and autumn semesters.
Course system for undergraduate students in SCE
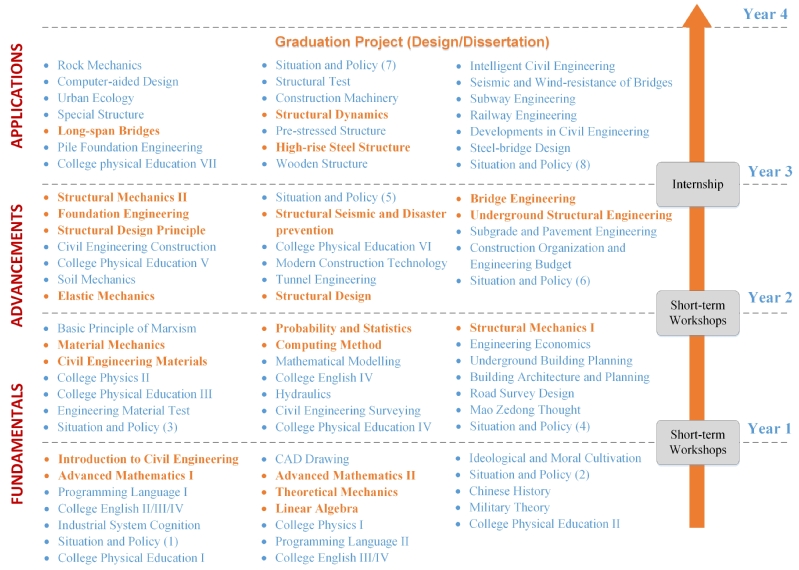
(a) Civil Engineering
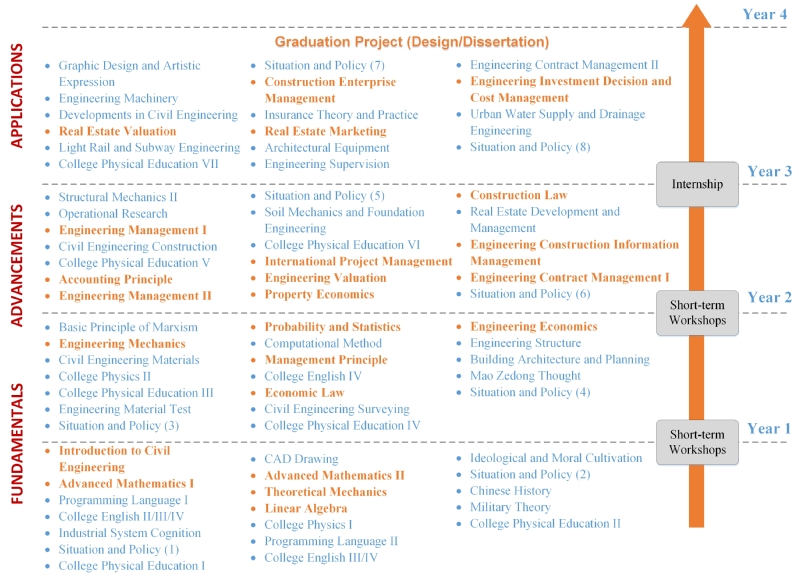
(b) Construction Management
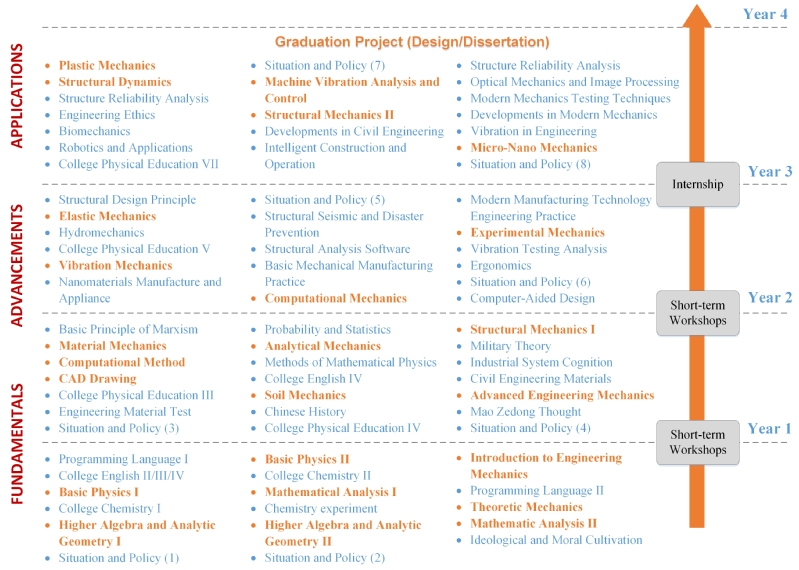
(c) Engineering Mechanics
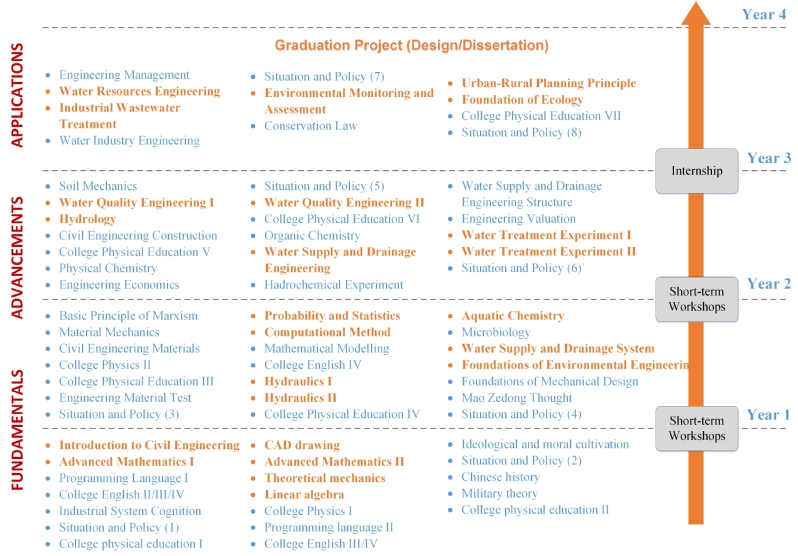
(d) Water Engineering
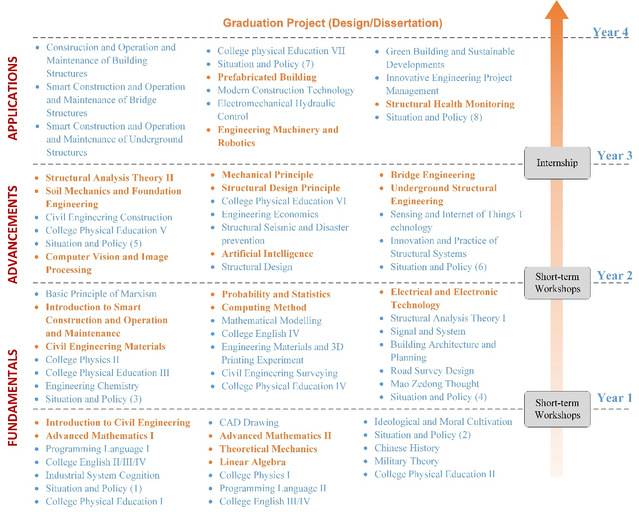
(e) Smart Construction
Senior Year Design/Research Projects
For the graduation projects, the undergraduate students can choose to conduct either a design project or a research-based dissertation guided by a SCE faculty member. The percentages of dissertations and design projects are shown below. The ratio of dissertations is around 20%, and the ratio of design projects is about 80%, and the ratio varied little each year.
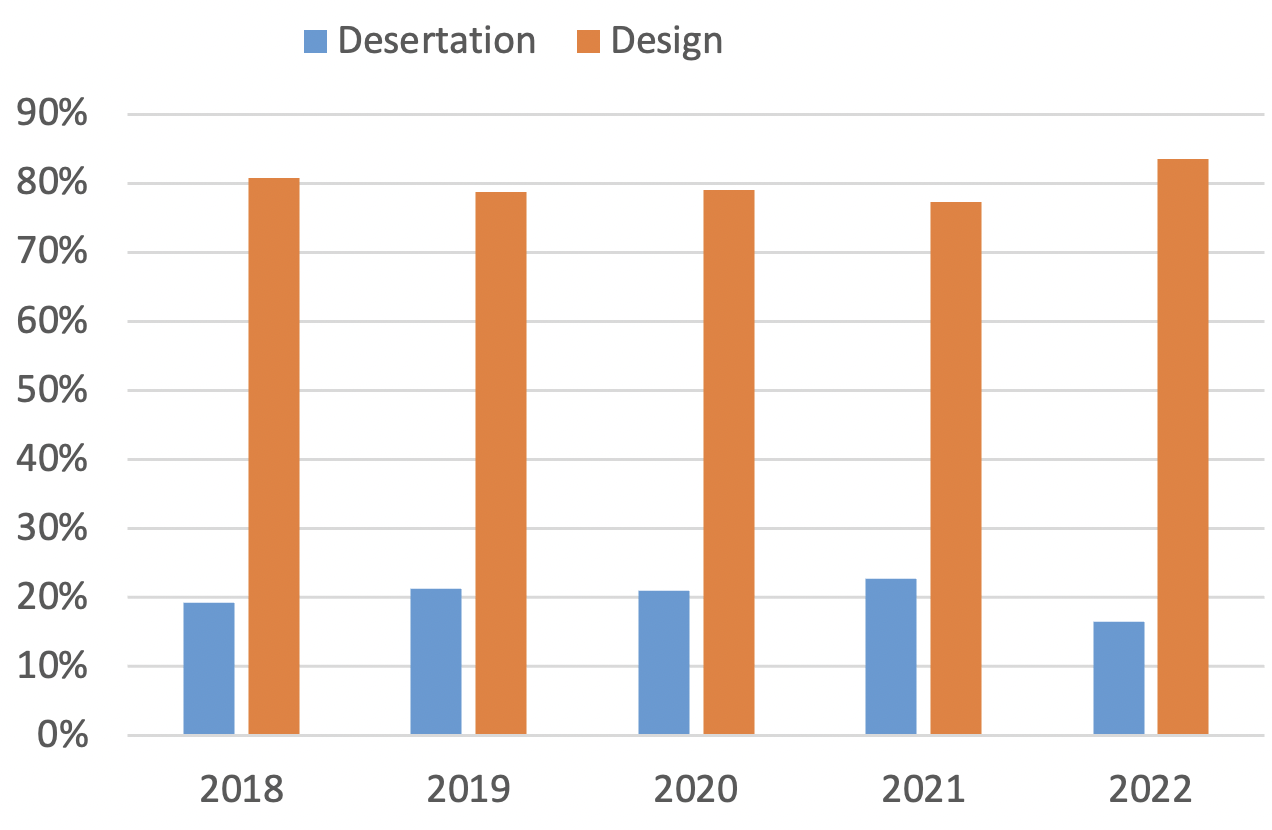
Percentages of dissertations and design projects in the graduation projects
Some excellent graduation projects are introduced below:
(1) Study on Non-linear Dynamic Response and Anti-collision Measures of Lijia Jialing River Bridge
With the rapid development of China's transportation infrastructures, more and more cross-river bridges have been built. Unfortunately, the bridge piers which stood in the water have become obstacles to water transportation and are likely hazard to the passing ships. In this study, the dynamic response of Chongqing Lijia Jialing River Bridge subjected to ship collision was examined to ensure safety of the Bridge and vessel. The Bridge is a continuous rigid frame bridge with a span of 785m (140m + 245m + 190m + 130m + 80m).
ANSYS-DYNA finite element software was used to simulate the ship-bridge collision. According to the navigation condition before and after the establishment of the Three Gorges Dam, a 1,000-ton ship model was adopted. According to Jialing River's mileage and flow velocity, and the ship's tonnage, the impact of the collision was computed by the AASHTO method. The ship's reachability was then analyzed to determine the impact position; compared the maximum impact force computed by different normative formulas; measured the deformation of the bow after collision, the time curve of the impact force and the displacement of the pier. Finally, two feasible protective measures were proposed for the Lijia Bridge.
(2)Research on fracture mechanics parameter identification method based on virtual field method
The main works of this study were: (1) VFM and FF were programmed based on MATLAB, and validated using ABAQUS. (2) Feasibility of the measuring material constitutive parameters by VFM was verified by uniaxial tensile test of slat specimens. The experimental results showed that the relative errors of elastic modulus and Poisson's ratio were within 2% and 10%, respectively. (3) By the experiment of unilateral notched slat specimens under uniaxial tension and the experiment of unilateral notched three-point bending beam, applicability of the FF method to compute the stress intensity factor (SIF) for different samples was verified and influence of the measurement error of material parameters on the computed results of the SIF was studied. The experimental results showed that the relative error of the SIF is less than 10% in the linear elastic stage, and the computed results were sensitive to Young's modulus but not to Poisson's ratio. (4) Based on analysis of the experimental results of the three experiments, combined with Irwin's estimation of the size of the crack tip plastic zone and the identification method of the plastic zone based on VFM, the study presented a method to modify the SIF under a small yield range.